Wetlands Dominant Plants
Horsetail Equisetum arvense switch grass Panicum virgatum and arrowleaf Sagittaria latifolia. Birds in wetlands Huge numbers of birds spend all or part of their life cycles in wetlands which provide habitat and food sources for them to survive.

Towards A Trait Based Ecology Of Wetland Vegetation Moor 2017 Journal Of Ecology Wiley Online Library Source: besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded by water either permanently or seasonally where oxygen-free processes prevail.

Wetlands dominant plants. Class VII - Fen Ponds are wetlands in which fen vegetation dominates the deepest portion of the wetland area. Our results showed threshold-like effects on the interaction between hydrological connectivity and P. Dominant plants was documented for each potential wetland area and was compared to the National Wetland Plant List NWPL Corps 2018 to determine the wetland indicator status of each species.
Specifically the Wet Prairie and Emergent Marsh community can be constructed from pre-existing wetlands. The dominant plants are sedges grasses reeds mosses and some shrubs. Arrow arum Peltandra virginica Pickerelweed Pontederia cordata.
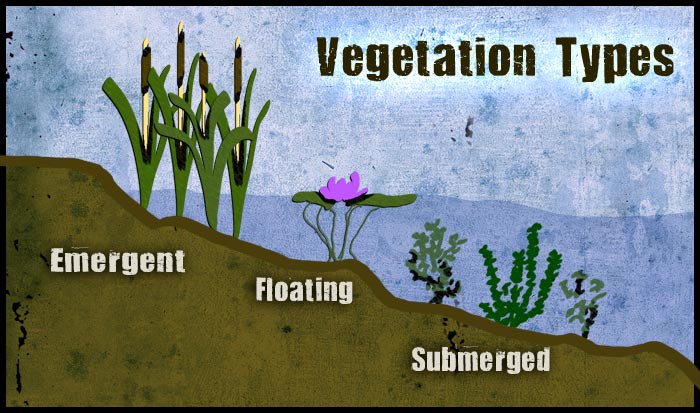
These plants decompose rapidly and completely each winter giving the appearance of a mud flat then they re-appear each spring. Cattails are one of the most well-known wetland plants because they are widespread and easily recognizable with their brown tail-like flowering structures Figure 5. The primary factor that distinguishes wetlands from other land forms or water bodies is the characteristic vegetation of aquatic plants adapted to the unique hydric soilWetlands play a number of functions including water purification water storage processing.
Cattails and sedges are common plants that grow up from the soil through the water. Waters are nutrient rich with. Marsh A wetland with mineral or sometimes well-decomposed peat soils and surface water levels that fluctuate seasonally exposing matted vegetation or mudflats when low.
Wetland plants are with a few exceptions angiosperms or flowering plants. For example genotypic variation or phenotypic plasticity can lead to considerable local or regional variation in the relative frequency with which individual plants of a particular species occur in wetlands. There are two species of cattail in Delaware.
Of the known 250 000 angiosperm species only about 35 are adapted to the wetland environment. Marshes are mainly wet mineral-soil areas but. Herb stratum Consists of all herbaceous non-woody plants including herbaceous vines regardless of size and woody plants less than 328 ft tall.
Woody vines Consists of. DBH and greater than or equal to 328 ft 1 m tall. All kinds of amphibians frogs toads and salamanders can be found.
These wetlands are especially attractive for shore birds. Scattered trees may be present. Dominant native species at this site include.
Near-neutral to slightly acid pH. Carolina Wetlands fourteen major types of wetlands and their most common plants are described as well as characteristic features of these wetlands. These are common plants found in Virginias tidal freshwater marshes where the salinity remains less than five parts per thousand.
Indicator ratings are as follows Corps 2012. In this study we parametrically quantified the hydrological connectivity in the tidal marsh wetlands and analyzed its relationship with Phragmites australis one of the dominant species in this area. As with plants the types of animals found in wetlands depend upon the type of wetland.
Saplingshrub stratum Consists of woody plants less than 3 in. Several thousand plant species grow in wetlands ranging from mosses and grasses to shrubs and trees. Marshes are wetlands that are periodically inundated by standing or slowly moving water and hence are rich in nutrients.
Dominant plants include black spruce tamarack sedges grasses and various mosses. Wet flats pocosins ephemeral wetlands seeps mountain bogs bog. The dominant plants are generally salt tolerant and include red swampfire and spiral ditchgrass.
These wetland types include. There are however some general types of animals that will be found in most wetlands. The broadleaf cattail is native Typha latifolia while the narrowleaf cattail Typha angustifolia is invasive.
Wetland plants are often the most conspicuous component of wetland ecosystems. They are also referred to as hydrophytes macrophytes and aquatic plants. Alkali wetlands are characterized by a pH above 7 and a high concentration of salts.
Appendix 1 also lists dominant plants from these fourteen wetland types. The use of plant species as indicators of wetland boundaries has important limitations.

Aggressive Non Native Wetland Plants Squelch Species Richness More Than Dominant Natives Do Illinois Source: news.illinois.edu
Ms Aquatic Plants Source: jcho.masgc.org

Wetlands Biome Untamed Science Source: untamedscience.com

Aggressive Non Native Wetland Plants Squelch Species Richness More Than Dominant Natives Do Illinois Source: news.illinois.edu